
In the next few years, the world’s population is expected to have exceeded 10 billion people. Data analysis, machine learning, transportation, rapid development, direct impact on the lives of overcrowding, and our built environment.
The main challenge for the architecture of the future is for designing new spaces or modernizing the existing one’s faster-evolving technologies. Almost all developed cities and those with emerging economies have their architecture masterpiece. They have been classified based on aesthetics, functional feasibility, and structural creativity. The construction industry is one of the major ones undergoing drastic changes due to the different facts and there is a new technology growing every year so with time even things are evolving
Climate change :
Climate change is one of the most important factors that we look into while talking about the architecture of the future. One of the main issues is that considering climatic conditions and sustainability together it will never have a structure built. Refurbishments over demolition this is a lot of time-consuming but also reduces the use of materials, and carbon emissions by eliminating the building process and demolition itself.
Some of the techniques that started seing lights nowdays and we hope will be used a lot more in the future to help reduce all the climate change problems caused by the construction of buildings:
- Carbon neutral or , even better, carbon negative buildings:
As every architect must know, buildings consume 36% of the global energy annually, and they emit nearly half of the carbon dioxide, through grrenfield development, cement production and the burning of fossil fuels such as oil, gas and coal.
Because CO2 traps solar energy in the atmosphere, thereby heatinh the planet, it is the chief agent of climat change.That’s why architects are taking a new approach on their designs by making buildings carbon neutral or even better carbon negative.
The terminology around this push is confusing but generally speaking a netcarbon-neutral building is one that does not contribute any CO2 to the atmosphere over it’s lifetime.
A carbon-negative building is one that removes more carbon from the atmosphere than it emits over it’s lifetime.
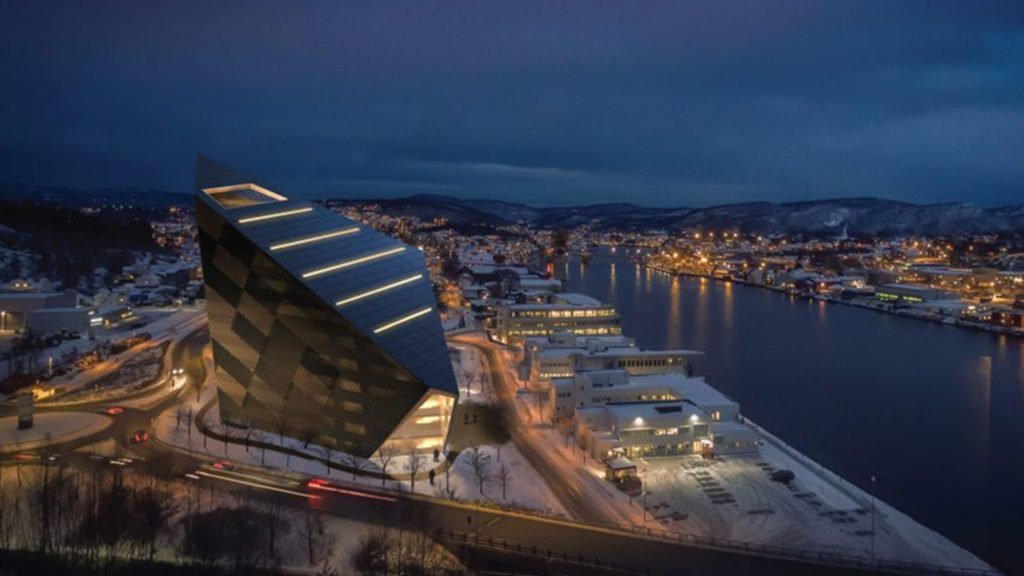
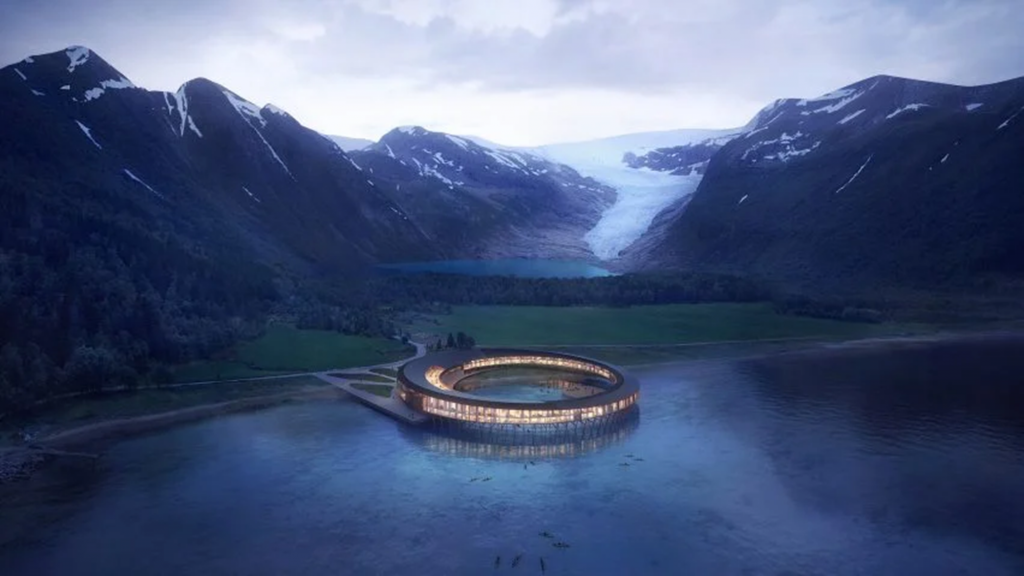


- Building with Timber :
Wood has always been used to build structure throughout history. However, There has been a recent reapperance in its popularity as a construction element since it can eliminate large ammounts of Carbon from the atmosphere and store it within a building for as long as it stands.
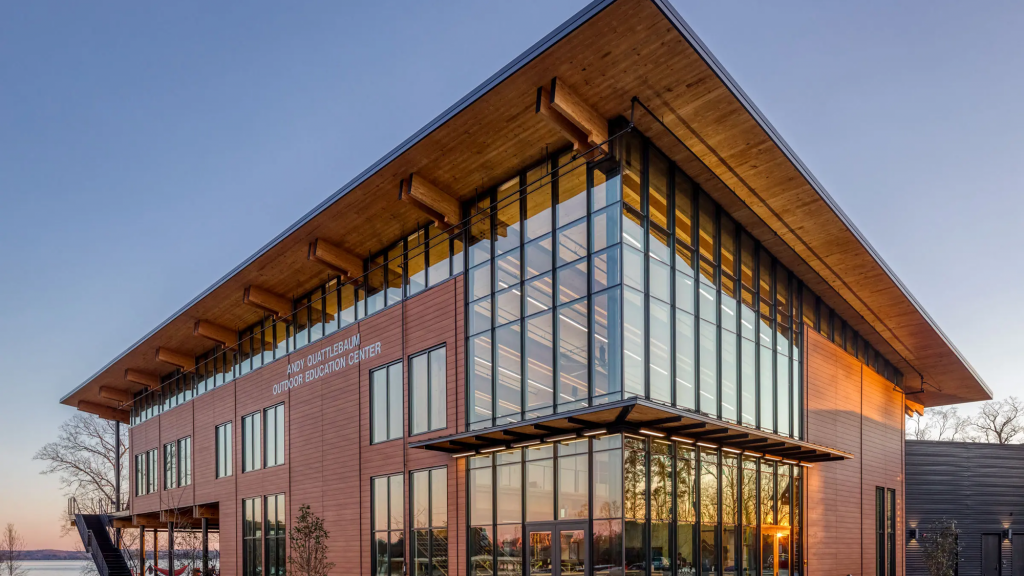

- Reversible design:
Reversible Building Design is design of buildings which can beeasilydeconstructed, or where parts can be removed and added easily without damaging the building or the products, components or materials.
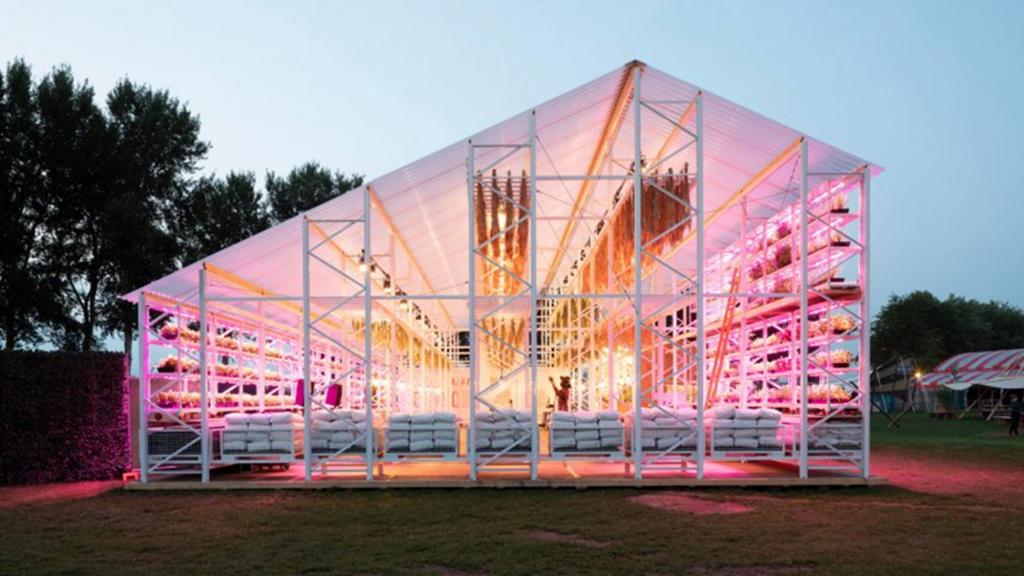


•The stand is made entirely from reusable raw materials and included walls clad in uncut sheets of plywood, plinths built up of uncemented bricks and a floor covered in stone chips. After the fair, the components were packed away to be used at future exhibitions. “The stand is made of natural materials such as wood, bricks and stone,” said Daniel Heckscher of Note Design Studio. “Everything is fully recyclable and reusable. It’s modular in the sense that the wood panels are demountable and not screwed or glued.”
Main materials excpected to be used in future architecture :
- Wood : already explained it’s importance above but there is other of its versions like the ones listed next.
- Plywood : Plywood is a mixture of wood and glue so we can say that it’s engineered wood. It is manufactured by glueing layers of veneers, which are thin sheets of peeled wood, together to create plywood boards for furniture manufacture. Plywood is being used more and more as a creative solution for small living spaces. As the population increases our inhabitable space decreases. For architects, the use of interior space is incredibly important. Small spaces have to accommodate the same things as larger spaces can give. Plywood also afords a sense of warmth in the design. Many people are attracted to the atmosphere the wood gives to the interior design.
- Newspaper wood : Newspaper wood is a new way of creating the look of wood in architecture. This interesting new building material was pioneered by Mieke Meijer. Though the material is predominantly used for furniture and smaller projects, we can see it rapidly grew into an important building material. Repurposing materials we no longer have use for, like old newspapers, is a growing trend for building materials.
- Plastic : Today Architects are using plastic as the material it is. Plastic is being re-envisioned as a tool to build lighter, and less dense structures in architecture. It is easy and less expensive to transport because of lower weight. Easier to maneuver on site. Rot resistant. Corrosion resistant.
- Glass: Glass has been used for its aesthetic appeal for centuries. Historically the wealthier buildings like churches would make use of more glass facades.The cool thing about glass is that we can adjust how much light comes in at one time.This new glass can harness heat from the sun and add to the insulation of the building. This is particularly exciting for energy efficiency and sustainability in the future. Future buildings feature more and more glass as we have learned that it can help with stress, anxiety, productivity, and depression. Glass Is being used in major ways today and the technology is only growing for future buildings.
- Glass Tek : Glass Tek has installed IR technology in glass to afford people with and interactive experience. You can flip through the weather or look over your plans for the week. This technology is so cool because it can be added to any pre-existing glass as well.
- Earth materials :
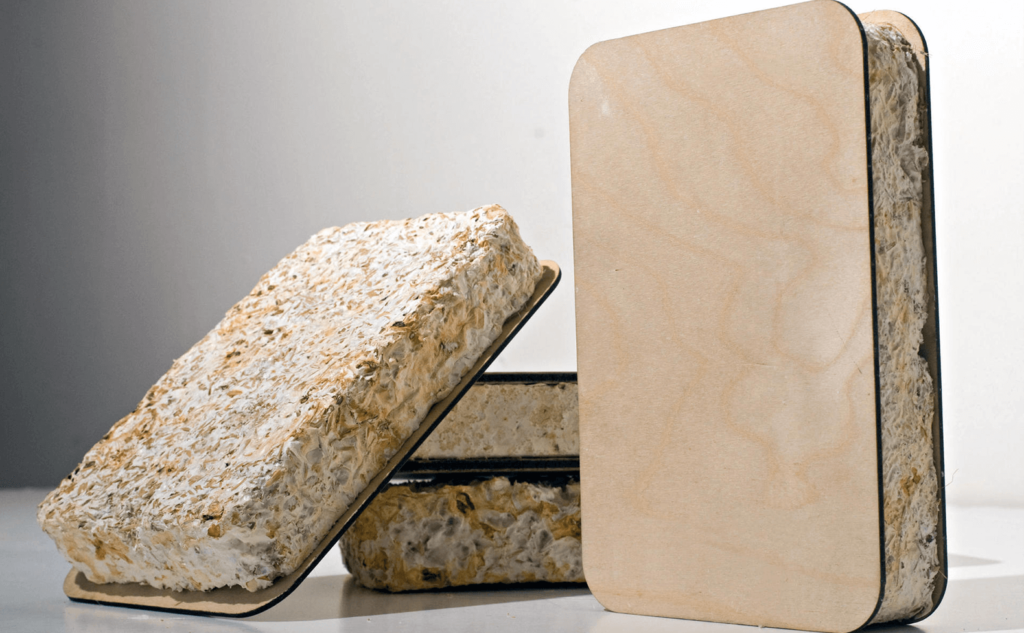
Materials that harness nature are the future. These materials are absolutely out of this world. Who would have thought you could make walls out of mushrooms. One reason these materials are so intriguing for the future of Architecture, is that they are economically attractive and sustainably sound. Early civilizations used only earth materials as they couldn’t create synthetic materials. Materials like mud and adobe have been used since the beginning of civilization. The architecture of the future has taken inspiration from the past. Here we define earth materials as the raw materials created in nature.
Mushroom walls :
Mushroom walls are being used in building as insulation. They are keenly better for humans to breath than any other more detrimental to our health like asbestos.
Eben Bayer and Gavin McIntyre are the two engineers behind the mushroom project. They created the company Ecovative. Mushroom roots are put between two interior walls and it grows in the dark creating insulation and warmth within the building.
This innovation in insulation shows just how valuable earth materials are and will be in the future.

Types of Future Buildings :
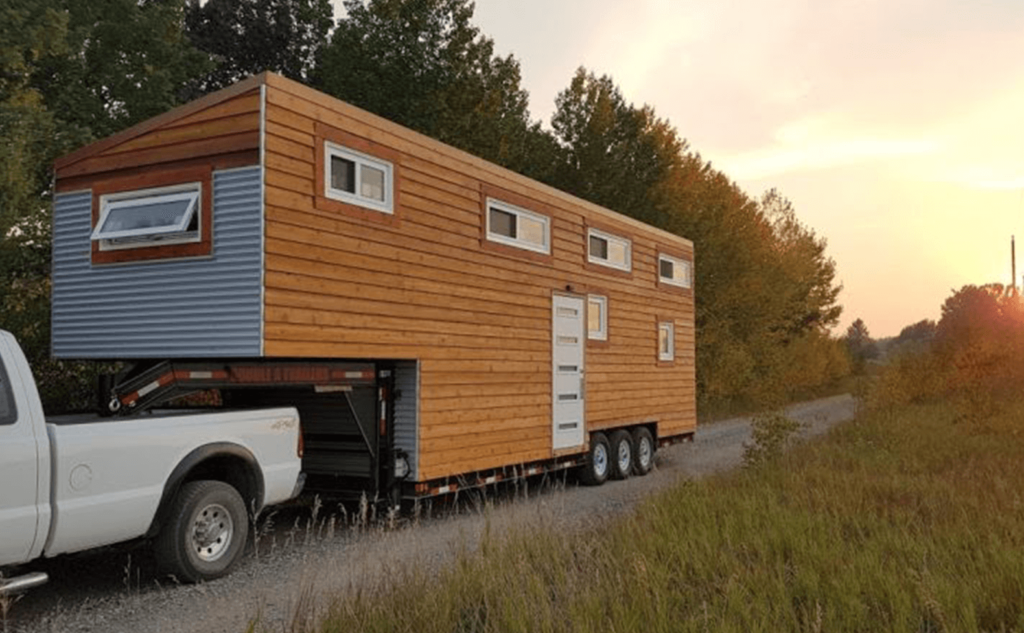
- Tiny homes :
The Tiny House Movement is all about quality of quantity. Independent people, or companies create small homes that typically rest on wheels in order for them to be transported anywhere.
These tiny homes are attractive for buyers because you don’t have to be tied down to one location, your house can roll anywhere you wish. From 1973 to 2015 house size rose and family size decreased. The tiny house movement is slowly reversing the, “bigger is better,” mindset. This architectural movement has presented challenges for architects today.

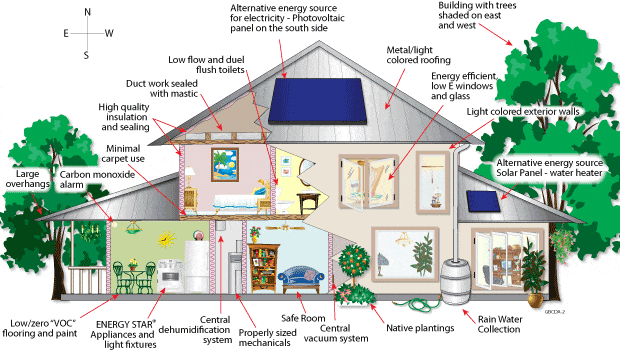
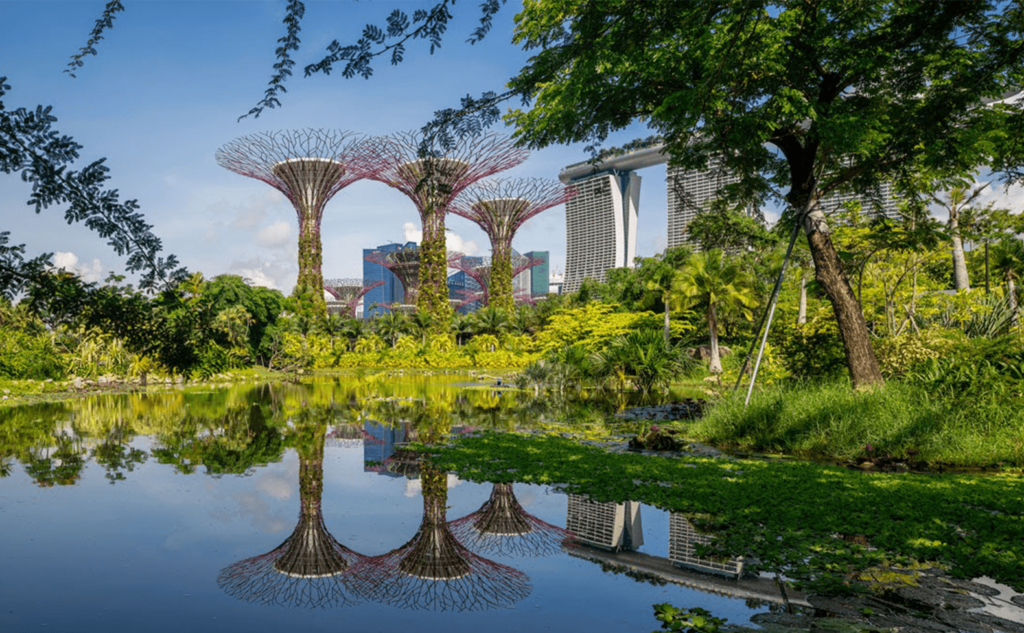
- Green buildings :
A ‘green’ building is a building that, in its design, construction or operation, reduces or eliminates negative impacts, and can create positive impacts, on our climate and natural environment. A cool thing about green buildings is that they could be anything, a house, an office, a hospital, absolutely anything.

- Modular Architecture :
Modular architecture is all about prefabricated materials being used to create a building. Essentially prefabrication companies, build all everything the architect needs to build and it is assembled on site.
it’s aim is to build a home in less time, for less money, with less harmful stuff, and less environmental impact is.
They prepare the building offsite and deliver it complete to the construction site.
Not only is building modular cost-effective, but it also eliminates the environmental impact of a traditional build. It would be ideal if homes could be constructed off-site and owners could move in the day after they buy.

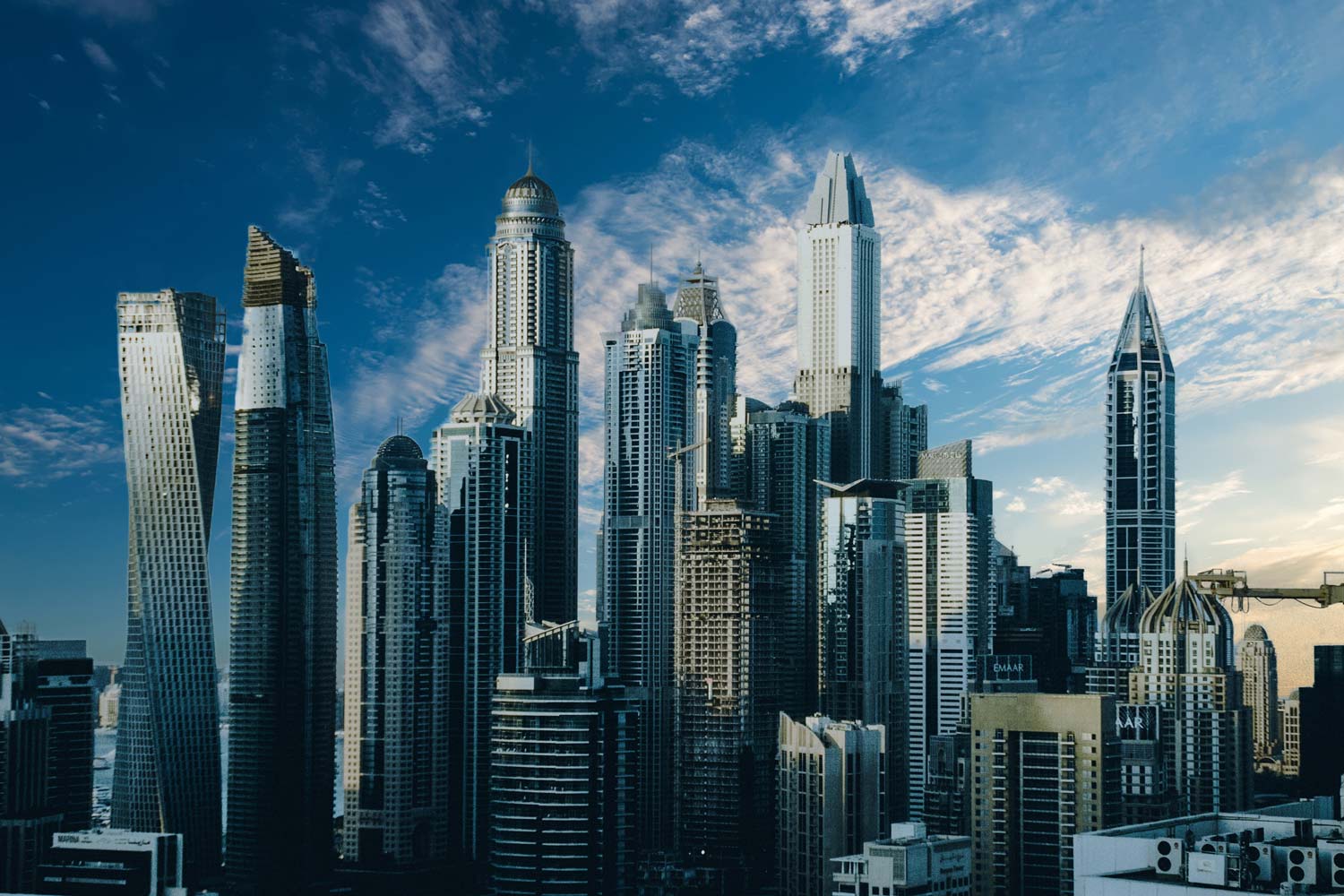
- High-rises and skyscrapers :
The future of architecture is up. Building taller, smaller, and more efficient is the way of future buildings. Skyscrapers are not only popular but innovative.
Future buildings take sustainability into account featuring vertical farming, timber materials, and glass.

To conclude :
The building of the future will reach the sky, the will use sustainable materials, and the spaces will get tighter. Population rise and the importance of environmental impact will dictate the parameters architects need to work in. Visionaries are already using the newest techniques and imagining the future today. Only time will tell what trends will stick and what will fall away, but one thing is sure, we will have to build smarter. All of the new technology at architects’ disposal will change the way buildings look and how quickly they are built.