Roman architecture continued the legacy left by Greek architects and the established architectural orders, especially the Corinthian. The Romans were also innovators and they combined new construction techniques and materials with creative design to produce a whole range of brand new architectural structures. Typical innovative Roman buildings included the basilica, triumphal arch, monumental aqueduct, amphitheatre, and residential housing block.
Many of the Roman architectural innovations were a response to the changing practical needs of Roman society, and these projects were all backed by a state apparatus which funded, organised, and spread them around the Roman world, guaranteeing their permanence so that many of these great edifices survive to the present day.

With the discovery of concrete, the Romans created new forms and were able to experiment with interior space, lights and shadows. The most singular technical advance was the coverage of large public spaces with arches, vaults or domes (except for temples).
They did not follow constructive ideals but stability, functionality and magnificence.
- Religious buildings: temple
They were the most important public buildings place,the Romans built them to worship their Gods and Goddesses. Each temple had a god’s statue that was kept deep within the temple. This statue was usually on top of a heavy foundation and surrounded by colonnades. A flight of odd-numbered steps led to the entrance of the temple. Only priests serving the gods were allowed inside the temples.

- Civil works :
Romans were specialists in the design of infrastructures such as:
*Sewage networks (vaulted galleries that carried sewage to rivers or the sea).
*Aqueducts (some are still being used) for water supply to cities)
*Roads that reached all points of the empire.
*Bridges (some are also still being used).
*Walls to protect the cities against enemy.
Public buildings :
- Commemorative w. :
- Triumphal Arches: a monumental structure pierced by at least one arched passageway and erected to honour an important person or to commemorate a significant event. It was sometimes architecturally isolated but usually was built to span either a street or a roadway, preferably one used for triumphal processions.
- Commemorative columns: Trajan’s Columnis a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan’s victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Apollodorus of Damascus at the order of the Roman Senate.
- Thermal baths : Romans established public baths and showers within their gymnasium complexes for relaxation and personal hygiene. Greek mythology specified that certain natural springs or tidal pools were blessed by the gods to cure disease. Around these sacred pools, Greeks established bathing facilities for those desiring to heal.
They contained:
*Apodyterium: for changing and storing clothes.
*Tepidarium: warm room.
*Caldarium: hot room.
*Frigidarium: cold room.
*Natatio: open-air swimming pool.
*Palaestrae: exercise rooms.
- Theatre : It’s an open-air theater constructed by the ancient Romans, sometimes built on a hillside, but more often on level ground usually with a richly decorated outer façade, with a colonnade gallery and vaulted entrances for the public.
The main parts of a theatre were:
*Scænæ: stage house.
*Orchestra: space between the cavea and the scænæ.
*Cavea: seating section.
- Amphitheatre: Roman amphitheatres are Roman theatres – large, circular or oval open-air venues with raised seating, built by the ancient Romans. They were used for events such as gladiator combats, venationes (animal slayings) and executions.The word amphitheatrum means “theatre all around”.
- Basilica : The term basilica refers to the function of a building as that of a meeting hall. In ancient Rome, basilicas were the site for legal matters to be carried out and a place for business transactions. Architecturally, a basilica typically had a rectangular base that was split into aisles by columns and covered by a roof.
- Circus : The Roman circus was a large open-air venue used for public events in the ancient Roman Empire. Circuses were venues for chariot races, horse races, gladiatorial combat, and performances that commemorated important events of the empire were performed there.
- Domus : Private family residence of modest to palatial proportions, found primarily in ancient Rome and Pompeii. In contrast to the insula, or tenement block, which housed numerous families, the domus was a single-family dwelling divided into two main parts, atrium and peristyle.
- Insula : block of grouped but separate buildings or a single structure in ancient Rome and Ostia. The insulae were largely tenements providing economically practical housing where land values were high and population dense.
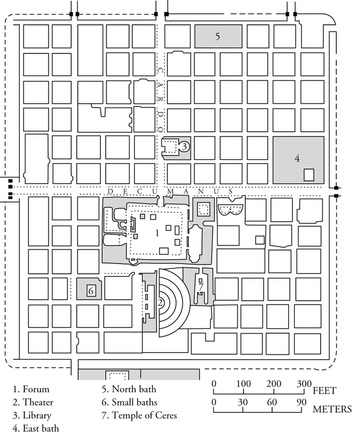
Romans’ cities :
Throughout their empire the Romans built towns in exactly the same style. They were designed in the form of a grid, with streets built at right angles to each other and parallel with one of the two main roads. … They were so well built that we have been able to excavate many Roman buildings and even towns.
Conclusion:
Roman architecture, then, has provided us with magnificent structures that have, quite literally, stood the test of time. By combining a wide range of materials with daring designs, the Romans were able to push the boundaries of physics and turn architecture into an art form. The result was that architecture became an imperial tool to demonstrate to the world that Rome was culturally superior because only she had the wealth, skills, and audacity to produce such edifices. Even more significantly, the Roman use of concrete, brick, and arches twinned with building designs like the amphitheatre and basilica would immeasurably influence all following western architecture right up to the present day.